Students enjoy the stunning natural beauty of Vancouver, one of the most spectacular cities in the world, as well as one of its cleanest and safest. Despite the modern urban setting of the city itself, Vancouver is enveloped in a natural setting of extraordinary mountains, lush forested areas and the North Pacific Ocean.
Vancouver is one of the few places in the world where a morning can be spent on the beach, with the same afternoon spent enjoying snow sports less than 30 minutes away. This is one of the reasons why Vancouver is so frequently ranked in the top 10 most desirable cities to live in the world. Public transport makes exploring and commuting to and from your studies simple and safe, with frequent and well situated bus routes and SkyTrains running from dawn until dusk.
Getting started
Climate
Vancouver has the mildest climate of any major city in Canada, but the weather can be unpredictable. Vancouver can see a great deal of rain in the winter, but during the summer months Vancouver gets less rain than most other Canadian cities.
-
Temperatures: From January to May: 6 °C to 18 °C
-
Temperatures: From May to August: 17 °C to 24 °C
Neighbourhoods
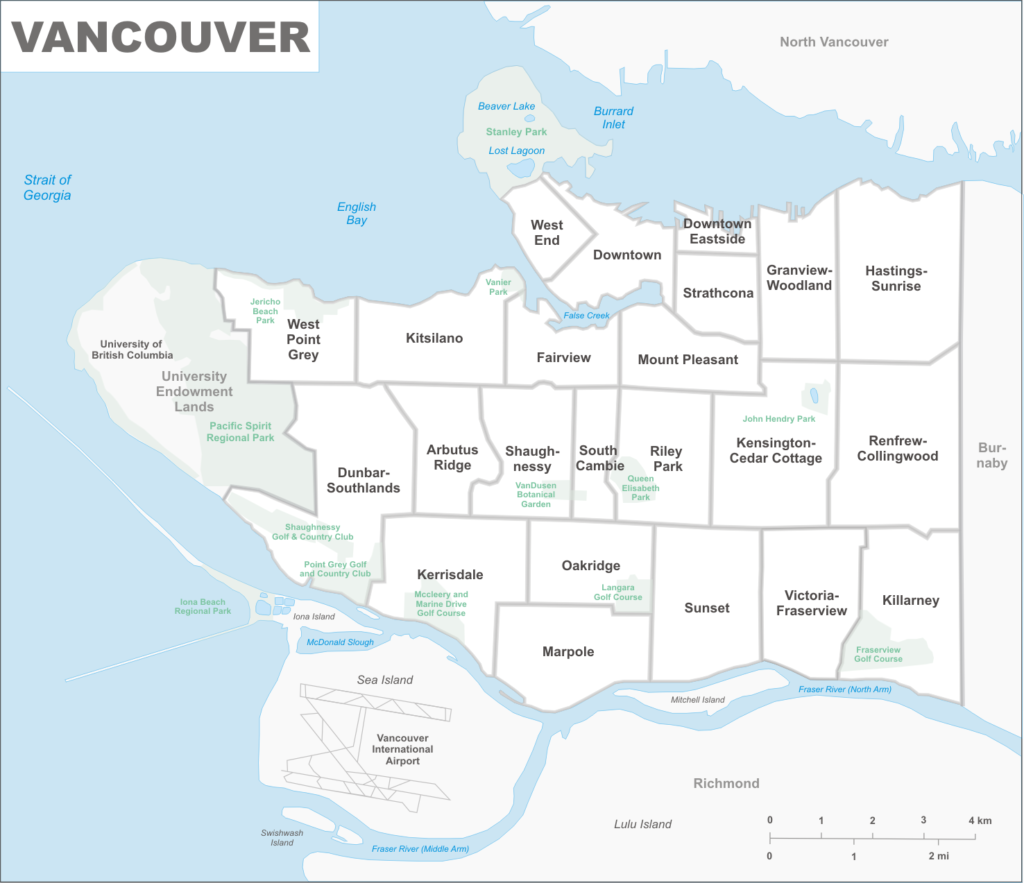
Columbia College is located in front of the Pacific Central Station in Strathcona, Vancouver’s oldest residential neighbourhood. It is bordered by Chinatown to the west, Clark Drive to the east, and Canadian National Railway and Great Northern Railway classification yards to the south.
Transportation
Vancouver’s public transportation is both efficient and convenient. The Translink system includes buses, the SeaBus ferry and the SkyTrain (light rail), all of which are ecologically friendly, reliable and inexpensive.
|
Types of transit |
|
|
Bus |
Translink’s bus routes connect directly with the skytrain and seabus right at the stations. buses operate seven days a week. check translink to plan your trip. |
|
SkyTrain |
SkyTrains run across the Metro Vancouver region, including to and from Vancouver, Burnaby, New Westminster, Richmond, Vancouver Airport and Surrey. The SkyTrain provides daily service every two to five minutes but does not run throughout the night. |
|
SeaBus |
The SeaBus is a passenger-only ferry that travels between Vancouver and North Vancouver. The SeaBus links with the SkyTrain and buses in downtown Vancouver at the Waterfront Station. It operates daily every 15 to 30 minutes. Bikes are welcome on the SeaBus. |
For more information on bus routes, schedules, and more, contact Translink Information at 604-953-3333 (6:30 a.m. to 11:30 p.m.) or online at www.translink.bc.ca.
All Columbia College students must pay adult fares on transit (even if you are under 19 years of age)unless you are a full-time high school student, in which case you can obtain an orange concession card.

Compass: Load. Tap. Ride.
Compass is a reloadable fare card that works everywhere on transit in Metro Vancouver. It’s convenient, easy to use, and provides discount fares. You can load fare products onto one card and tap your way across the system. Click here for more information about Compass cards.
Where to Buy Compass Cards and Tickets
You can buy a Compass Card at the following convenient locations:
-
Compass Vending Machines (CVMs)* located at:
-
SkyTrain, SeaBus, and West Coast Express stations
-
BC Ferries Tsawwassen and Horseshoe Bay terminals
-
-
At 18 London Drugs locations across metro Vancouver
-
Online at compasscard.ca
-
By calling 604.398.2042
-
Compass Customer Service Centre at Stadium–Chinatown SkyTrain Station
*Concession Compass Cards are not available for purchase at CVMs.
Compass Vending Machines accept cash, credit, and debit. Online payment and AutoLoad enrollment can be done with Visa, Mastercard, Visa Debit, and Debit Mastercard. It can take up to two hours for your Compass product to be available for use. If you purchase fare products at a CVM, they’ll be available for use immediately.
Banking
Here is everything you need to know about setting up a bank account and transferring funds from your country.
Banks are large for-profit entities. Major banks in Canada include Bank of Montreal (BMO), Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce (CIBC), Royal Bank of Canada (RBC), Scotiabank, and TD Canada Trust.
A credit union is a cooperative financial institution in which individuals pool their money to provide loans and services to other members. They are non-profit entities, and their cooperative structure is designed to ensure fair dealing. Credit Unions in Vancouver include Vancity and North Shore Credit Union.
You can compare features for different chequing and savings accounts, including interest rates, monthly fees and transactions, using the Financial Consumer Agency of Canada (FCAC) – Account Selector Tool.
In Canada, you have the right to open a bank account provided you show proper identification. You can open a new bank account even if you do not have a job and it is not mandatory to deposit money into your account right away.
To open a bank account in Canada, you will need to go in-person to a financial institution and provide an acceptable form of identification (Passport, Study Permit and student ID, if applicable).
Most banks have student accounts with lower services fees, such as:
- Scotiabank Student Banking Advantage Plan
- TD Student Chequing Account
- CIBC Smart for Students
- RBC Student Banking Account
- BMO Student Banking
When deciding which bank to open an account with, there are many things to consider:
- How much is the monthly administrative service fee?
- What are the withdrawing and depositing rules?
- What are the fees when using Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) at other institutions?
- Is there a limit of e-transfers? What is the fee if I pass my monthly transfer limit?
- Does this account have online banking?
- Are there any point benefits with the account? (i.e. SCENE points, Air Miles, etc)
When using a Canadian account, beware of potential fees and charges such as:
- Withdrawing cash from other banks’ ATMs
- Withdrawing or debiting your savings account directly
- Non-Sufficient Funds (NSF), which means not having enough money in your account
- Going over monthly debit transactions allowed
- Paper statements – some banks charge about $2/month if you request paper bills
- Monthly maintenance fees
Debit Card
When you open an account, the bank will issue you a Debit card (which is also your ATM card). Your Debit card can be used in bank machines around the city, and is protected with a Personal Identification Number (PIN).
You can use it to pay for items directly. Charges to debit cards are deducted from your account immediately, unlike a credit card. Keep in mind that there is a limit on how much you can spend per day or week.
Credit Card
Credit cards are a convenient method of paying. Amount spent accumulates on your account, and should be paid off once a month. Most online purchases are carried out with credit cards. Payments will affect your credit score. You can also withdraw cash from it like a debit card, but there are high interest charges so it is not commonly done.
The starting limits for international students may be very low for the first 6 months or more. However, credit scores are very important in Canada, and if you develop a good one, you may be eligible to raise the limit.
In Canada, your credit score is an important aspect of your financial profile. Credit scores range from 300 (just getting started) up to 900 points, which is the best score. They may be used to determine some of the most important financial factors in your life, such as whether or not you’ll be able to lease a vehicle, qualify for a mortgage or even land that new job.
There are many different issues that can hurt your credit, such as:
- Late or missed payments
- Too many (or too few) open credit accounts
- High credit card balances
- High balances on loans
- Too many credit applications
To develop good credit, you must:
- Pay bills on time, in full-balance to avoid interest charges
- Avoid credit-seeking behaviour
For almost all banks in Canada, you can access your account online or through a smart phone. Through both online and mobile banking, you can manage your accounts, pay bills, send money and check your transaction history.
You can send money to and from Canada either through your bank or through money transfer firms, such as Western Union. Transferring fees can be high, so find out the cost before you use the service.
Transferring funds from your home country before arriving in Canada
- Obtain a bank draft (a check drawn by a bank on its own funds in another bank) for the amount you wish to transfer and bringing it with you to Canada.
- Obtain an electronic bank card from your home bank and bringing it with you to Canada. Be mindful of service charges as well as currency exchange rates.
Transferring funds from your home country when in Canada
- Wire funds from your local bank to a Canadian bank. You will need to provide your bank from your home country with the following information about your Canadian account:
- Account name, address of the branch, account number, transit number, IBAN and swift code.
- Use a bank card from your home bank to withdraw money at ATMs in Canada. When using ATMs from other banks, you may be charged $3-$5 in withdraw fees.
Cell Phone Plans
To get a cell phone plan in Vancouver, you need to have two pieces of ID. You passport is mandatory to get a cell phone plan. The second piece of ID could be anything from a government issued ID card, your Study Permit, a Social Insurance card, or a valid credit card under your name.
Make sure you have your accommodation letter (or rental agreement) as a proof of address. Without proof of address, phone companies usually will not activate your cell phone plan.
A good option for short-term students is a monthly plan without contract. A lot of phone companies offer exclusive student plans which are usually cheaper and better. We advise you look into the student plans different phone companies have to offer before making your decision.
See different phone companies:
You can choose between Prepaid and Postpaid. The difference? With a Prepaid Plan, you pay first and it runs out after 30 days. Your phone service will stop working unless you add more money. With a Postpaid Plan, you use your service first and pay later. Be careful, your phone service won’t be cut off, so your bill will continue to increase! Not paying your phone bills on time can affect your credit score. If you choose a postpaid plan, make sure to check the fine for late payments with your phone company.

